Buat proyek ucapan ulang tahun menggunakan Arduino Mega, LCD I2C, buzzer, dan LED. Ikuti langkah-langkah mudah lengkap dengan wiring dan kode program Arduino. Cocok untuk pemula dan edukasi!
Ulang tahun adalah momen spesial yang layak dirayakan dengan cara kreatif. Nah, bagaimana jika kali ini kamu membuat alat otomatis yang bisa menyanyikan lagu ulang tahun lengkap dengan tampilan LCD dan LED berkedip?
Melalui artikel ini, kamu akan belajar cara merangkai Arduino Mega, LCD I2C, buzzer, dan LED untuk menciptakan alat ucapan ulang tahun otomatis yang menyenangkan dan edukatif. Yuk, kita mulai!
Alat dan Bahan
Berikut adalah komponen yang dibutuhkan untuk proyek ini:
| Komponen | Jumlah | Keterangan |
|---|---|---|
| Arduino Mega 2560 | 1 buah | Mikrokontroler utama |
| LCD 16×2 I2C (alamat 0x27) | 1 buah | Menampilkan ucapan |
| Buzzer (aktif/pasif) | 1 buah | Untuk memainkan lagu |
| LED | 1 buah | Efek visual |
| Resistor 220 Ohm | 1 buah | Untuk LED |
| Kabel jumper | Secukupnya | Untuk koneksi antar komponen |
| Breadboard | 1 buah | Tempat menancapkan komponen |
| Komputer + Arduino IDE | 1 set | Untuk memprogram Arduino |
Langkah-Langkah Perakitan
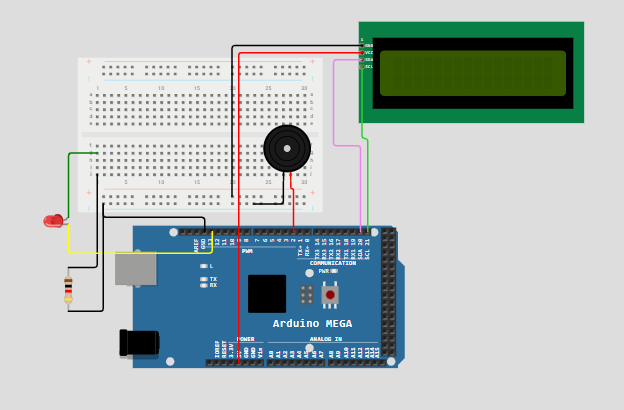
1. Rangkai Komponen Sesuai Skema
Berikut panduan koneksi:
- LCD I2C
- SDA → pin 20 (Arduino Mega)
- SCL → pin 21 (Arduino Mega)
- VCC → 5V
- GND → GND
- Buzzer
- Kaki positif → pin 11
- Kaki negatif → GND
- LED
- Anoda (+) → pin 13 melalui resistor 220Ω
- Katoda (−) → GND
2. Pasang Driver dan Library
- Buka Arduino IDE.
- Masuk ke Sketch > Include Library > Manage Libraries.
- Cari dan install:
LiquidCrystal I2C(pilih yang kompatibel denganlcd.init()). - Pastikan Board = Arduino Mega dan Port sudah terdeteksi.
3. Kode Program Arduino
Berikut adalah kode lengkap yang bisa kamu unggah langsung ke Arduino Mega:
/*
Happy Birthday
Connect a piezo buzzer or speaker to pin 11 or select a new pin.
Robson Couto, 2019
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27,16,2); // set the LCD address to 0x27 for a 16 chars and 2 line display
#define NOTE_B0 31
#define NOTE_C1 33
#define NOTE_CS1 35
#define NOTE_D1 37
#define NOTE_DS1 39
#define NOTE_E1 41
#define NOTE_F1 44
#define NOTE_FS1 46
#define NOTE_G1 49
#define NOTE_GS1 52
#define NOTE_A1 55
#define NOTE_AS1 58
#define NOTE_B1 62
#define NOTE_C2 65
#define NOTE_CS2 69
#define NOTE_D2 73
#define NOTE_DS2 78
#define NOTE_E2 82
#define NOTE_F2 87
#define NOTE_FS2 93
#define NOTE_G2 98
#define NOTE_GS2 104
#define NOTE_A2 110
#define NOTE_AS2 117
#define NOTE_B2 123
#define NOTE_C3 131
#define NOTE_CS3 139
#define NOTE_D3 147
#define NOTE_DS3 156
#define NOTE_E3 165
#define NOTE_F3 175
#define NOTE_FS3 185
#define NOTE_G3 196
#define NOTE_GS3 208
#define NOTE_A3 220
#define NOTE_AS3 233
#define NOTE_B3 247
#define NOTE_C4 262
#define NOTE_CS4 277
#define NOTE_D4 294
#define NOTE_DS4 311
#define NOTE_E4 330
#define NOTE_F4 349
#define NOTE_FS4 370
#define NOTE_G4 392
#define NOTE_GS4 415
#define NOTE_A4 440
#define NOTE_AS4 466
#define NOTE_B4 494
#define NOTE_C5 523
#define NOTE_CS5 554
#define NOTE_D5 587
#define NOTE_DS5 622
#define NOTE_E5 659
#define NOTE_F5 698
#define NOTE_FS5 740
#define NOTE_G5 784
#define NOTE_GS5 831
#define NOTE_A5 880
#define NOTE_AS5 932
#define NOTE_B5 988
#define NOTE_C6 1047
#define NOTE_CS6 1109
#define NOTE_D6 1175
#define NOTE_DS6 1245
#define NOTE_E6 1319
#define NOTE_F6 1397
#define NOTE_FS6 1480
#define NOTE_G6 1568
#define NOTE_GS6 1661
#define NOTE_A6 1760
#define NOTE_AS6 1865
#define NOTE_B6 1976
#define NOTE_C7 2093
#define NOTE_CS7 2217
#define NOTE_D7 2349
#define NOTE_DS7 2489
#define NOTE_E7 2637
#define NOTE_F7 2794
#define NOTE_FS7 2960
#define NOTE_G7 3136
#define NOTE_GS7 3322
#define NOTE_A7 3520
#define NOTE_AS7 3729
#define NOTE_B7 3951
#define NOTE_C8 4186
#define NOTE_CS8 4435
#define NOTE_D8 4699
#define NOTE_DS8 4978
#define REST 0
// change this to make the song slower or faster
int tempo = 140;
// change this to whichever pin you want to use
int buzzer = 2;
// notes of the moledy followed by the duration.
// a 4 means a quarter note, 8 an eighteenth , 16 sixteenth, so on
// !!negative numbers are used to represent dotted notes,
// so -4 means a dotted quarter note, that is, a quarter plus an eighteenth!!
int melody[] = {
// Happy Birthday
// Score available at https://musescore.com/user/8221/scores/26906
NOTE_C4,4, NOTE_C4,8,
NOTE_D4,-4, NOTE_C4,-4, NOTE_F4,-4,
NOTE_E4,-2, NOTE_C4,4, NOTE_C4,8,
NOTE_D4,-4, NOTE_C4,-4, NOTE_G4,-4,
NOTE_F4,-2, NOTE_C4,4, NOTE_C4,8,
NOTE_C5,-4, NOTE_A4,-4, NOTE_F4,-4,
NOTE_E4,-4, NOTE_D4,-4, NOTE_AS4,4, NOTE_AS4,8,
NOTE_A4,-4, NOTE_F4,-4, NOTE_G4,-4,
NOTE_F4,-2,
};
// sizeof gives the number of bytes, each int value is composed of two bytes (16 bits)
// there are two values per note (pitch and duration), so for each note there are four bytes
int notes = sizeof(melody) / sizeof(melody[0]) / 2;
// this calculates the duration of a whole note in ms
int wholenote = (60000 * 4) / tempo;
int divider = 0, noteDuration = 0;
void setup() {
lcd.init(); //initialize the lcd
lcd.backlight(); //open the backlight
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print(" Happy Birthday");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("JagoRobotik.com");
// iterate over the notes of the melody.
// Remember, the array is twice the number of notes (notes + durations)
for (int thisNote = 0; thisNote < notes * 2; thisNote = thisNote + 2) {
// calculates the duration of each note
divider = melody[thisNote + 1];
if (divider > 0) {
// regular note, just proceed
noteDuration = (wholenote) / divider;
} else if (divider < 0) {
// dotted notes are represented with negative durations!!
noteDuration = (wholenote) / abs(divider);
noteDuration *= 1.5; // increases the duration in half for dotted notes
}
// we only play the note for 90% of the duration, leaving 10% as a pause
tone(buzzer, melody[thisNote], noteDuration * 0.9);
// Wait for the specief duration before playing the next note.
delay(noteDuration);
// stop the waveform generation before the next note.
noTone(buzzer);
}
}
void loop() {
// no need to repeat the melody.
}Dengan menggunakan Arduino Mega, LCD I2C, buzzer, dan LED, kamu bisa membuat alat sederhana namun menarik untuk mengucapkan ulang tahun secara otomatis. Proyek ini sangat cocok untuk belajar dasar mikrokontroler, suara, dan tampilan I2C.
Tak hanya bermanfaat secara teknis, tapi juga bisa kamu jadikan hadiah ulang tahun unik untuk orang tersayang!
I am impressed with this site, very I am a big fan .